Having irregular periods occasionally is relatively common. However, if you often have very short or long menstrual cycles that change from one month to the next, this can be due to an underlying health problem. If you are among the 30% of women who experience irregular periods, Dr. Pamela Snook can help to diagnose and treat the underlying cause. Health providers consider a woman to have an irregular period if their cycles are longer than 38 days, shorter than 21 days, or the length of each menstrual cycle varies more than around 7 to 9 days. Here is a look at the possible causes of irregular periods.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
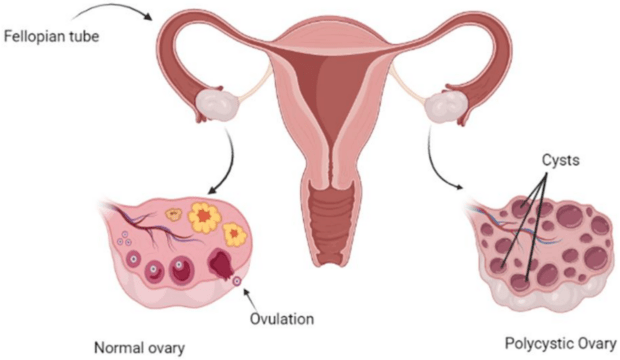
Irregular periods are one of the common symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. This condition occurs when you have cysts grow in your ovaries. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome have high androgen levels, a male hormone. This can halt ovulation, causing irregular periods. Women with this condition often miss periods and experience heavy bleeding when the periods come.
Endometriosis
Around 11% of women in America are affected by endometriosis. This condition causes excess tissue to grow outside the uterus. Therefore, your body has more tissues to shed during your menstrual cycle, resulting in heavier and longer periods. These periods come more often than the normal 28 days. Other common symptoms of endometriosis include a sharp pain in your pelvis, lower abdomen, and lower back.
Hormonal Birth Control
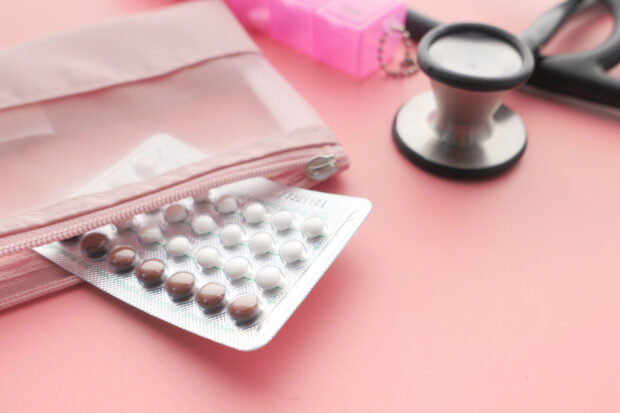
Depending on how your body reacts to the type of hormones in your birth control method, you might experience less or more bleeding. Birth control pills with progestin and estrogen might cause irregular bleeding during the first few months. Cooper IUD can also cause spotting between periods or heavier periods. On the other hand, progestin-only methods such as injections, implants, or mini pills cause the thinning of your uterine wall, causing less bleeding or absence of your periods.
Thyroid Disorders
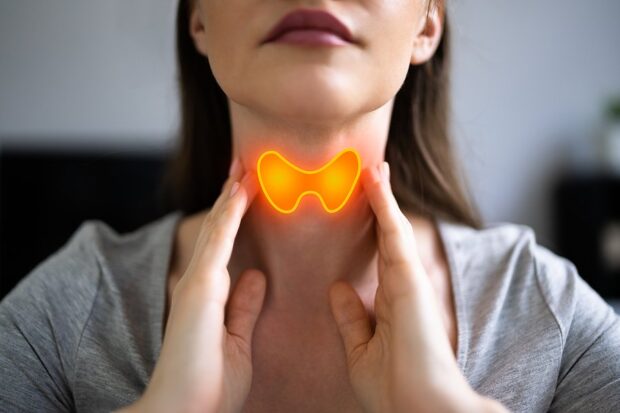
According to research, thyroid disorders are one of the major causes of irregular and missed periods. The thyroid gland functions to control your metabolism and has an impact on your reproductive hormones. Therefore, if you have a thyroid disorder such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, it can cause changes in your estrogen levels and hence irregularity in your menstrual periods.
Age
Changes to your hormonal levels are normal at the start and end of your menstruating years. Female teens often get irregular periods during the first or second year of puberty as the body starts to adapt to making increased hormone levels. Similarly, progesterone and estrogen levels start to decrease in women at around 40 to 50 years, causing irregular periods as a symptom of menopause.
Stress

High-stress levels have been found to cause irregular periods. According to scientific research, the body releases stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline when stressed. These hormones interact with the sex hormones that regulate menstruation, resulting in irregular periods. If you often feel stressed, it is advisable to seek help from a mental health specialist.
Ultimately, irregular periods can be caused by various factors, including medical factors. However, most of the causes are not serious, while others are. Slight variations in the duration of your menstrual cycles or between cycles aren’t a thing to worry about. Consult your healthcare provider if you experience significant changes in your menstrual cycle or if they become extremely painful. Your doctor can help diagnose the cause and suggest the appropriate treatment or other approaches if necessary.




























